This guide will walk you through setting up Ansible and Zookeeper on a series of Vagrant VMs. We will cover the necessary command prompt instructions and provide explanations and examples for each step.
Update and Install Required Packages
First, update your package list and install essential software:
sudo apt-get updateThis command updates the list of available packages and their versions, but it does not install or upgrade any packages.
sudo apt install software-properties-commonThis command installs the software-properties-common package, which provides useful scripts for managing software repositories.
Next, install Ansible, Git, Curl, sshpass, and Telnet:
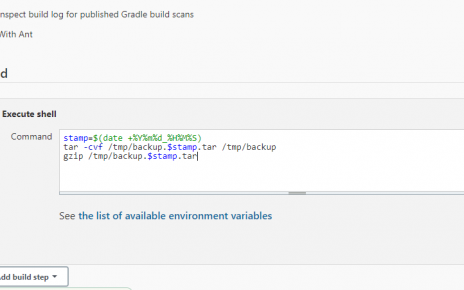
sudo apt-get install ansible git curl sshpass telnet -yThe -y flag automatically answers “yes” to any prompts during the installation.
Create Necessary Directories
Navigate to your Vagrant shared folder and create directories for Zookeeper configuration and data:
pwd
> /vagrant/master/ansible
mkdir data1 data2 files
mkdir files/etc files/opt
mkdir files/opt/zookeeper
mkdir data1/zookeeper
mkdir files/opt/zookeeper/conf/pwd: Displays the current directory.mkdir: Creates directories.
Install Java
Install the default Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Java Development Kit (JDK):
sudo apt-get install default-jre
sudo apt-get install default-jdk
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdkDownload and Configure Zookeeper
Download Zookeeper and extract it:
wget http://www-us.apache.org/dist/zookeeper/stable/apache-zookeeper-3.5.6.tar.gz
tar xzf apache-zookeeper-3.5.6.tar.gzwget: Downloads files from the web.tar xzf: Extracts the tar.gz file.
Copy configuration files:
cp apache-zookeeper-3.5.6/conf/zoo_sample.cfg files/opt/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg
cp apache-zookeeper-3.5.6/conf/log4j.properties files/opt/zookeeper/conf/cp: Copies files from one location to another.
Configure Vagrant VMs
Define your Vagrant configuration in a Vagrantfile:
config.vm.define "master" do |master|
master.vm.hostname = "master"
master.vm.box = "bento/ubuntu-18.04"
master.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.33.100"
master.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
vb.memory = "2048"
vb.cpus = 2
end
end
# Repeat for nodes 1-7 with appropriate hostname and IP configurationsconfig.vm.define: Defines a VM.master.vm.hostname: Sets the hostname.master.vm.box: Specifies the Vagrant box.master.vm.network: Configures network settings.master.vm.provider: Sets the provider configurations, such as memory and CPU.
Set Up SSH Access
Copy SSH keys to all nodes for passwordless access:
sshpass -f <(printf '%s\n' vagrant) ssh-copy-id -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no vagrant@192.168.33.10
# Repeat for all nodessshpass: Non-interactive ssh password provider.ssh-copy-id: Adds SSH keys to a remote machine’s authorized keys.-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no: Disables host key checking.
Configure Ansible Inventory
Create an inventory file for Ansible:
echo "[all]
192.168.33.100 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.10 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.20 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.30 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.40 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.50 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.60 ansible_user=vagrant
192.168.33.70 ansible_user=vagrant[gateways]
192.168.33.100 ansible_user=vagrant 192.168.33.10 ansible_user=vagrant
[ensemble]
192.168.33.20 ansible_user=vagrant 192.168.33.30 ansible_user=vagrant 192.168.33.40 ansible_user=vagrant
[brokers]
192.168.33.50 ansible_user=vagrant 192.168.33.60 ansible_user=vagrant 192.168.33.70 ansible_user=vagrant” > hosts
echo: Outputs text to a file.
Run Ansible Commands
Test the setup by running Ansible commands:
ansible all -i hosts -m command -a "hostname -f"
ansible gateways -i hosts -m command -a "hostname -f"
ansible ensemble -i hosts -m command -a "hostname -f"
ansible brokers -i hosts -m command -a "hostname -f"ansible: Runs Ansible commands.-i hosts: Specifies the inventory file.-m command: Specifies the Ansible module.-a: Passes arguments to the module.