Important Note: This article is part of the series in which TechReport.us discuss theory of Video Stream Matching.
General – Architecture of VSM
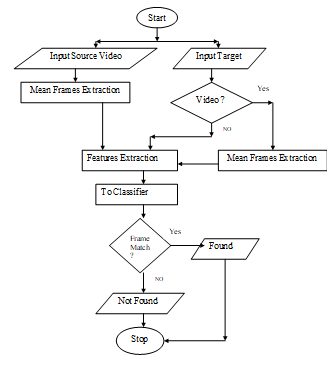
The architecture of VSM is consists on three main parts. Test side possibility is image or video and source have one possibility and it is only video.
- Load Target Video To classification Model
- Load Source Video To classification Model
- Load Target Image To classification Model
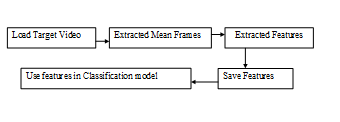
Figure 4.2 Load Target Video To classification Model
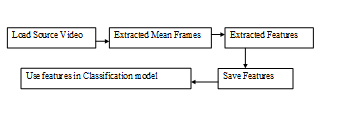
Figure 4.3 Load Source Video To classification Model
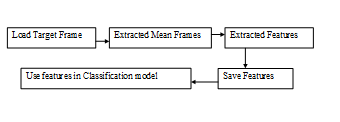
Figure 4.4 Load Target Image To classification Model