Important Note: This article is part of the series in which TechReport.us discuss theory of Video Stream Matching.
This part of VSM is consists on two parts.
- Target Image – Source Video – Model
- Target Video – Source Video – Model
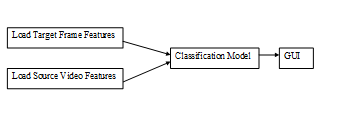
Figure 4.5 Target Image – Source Video – Model
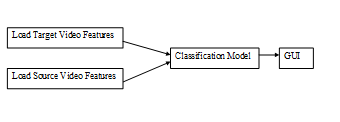
Figure 4.6 Target Video – Source Video – Model