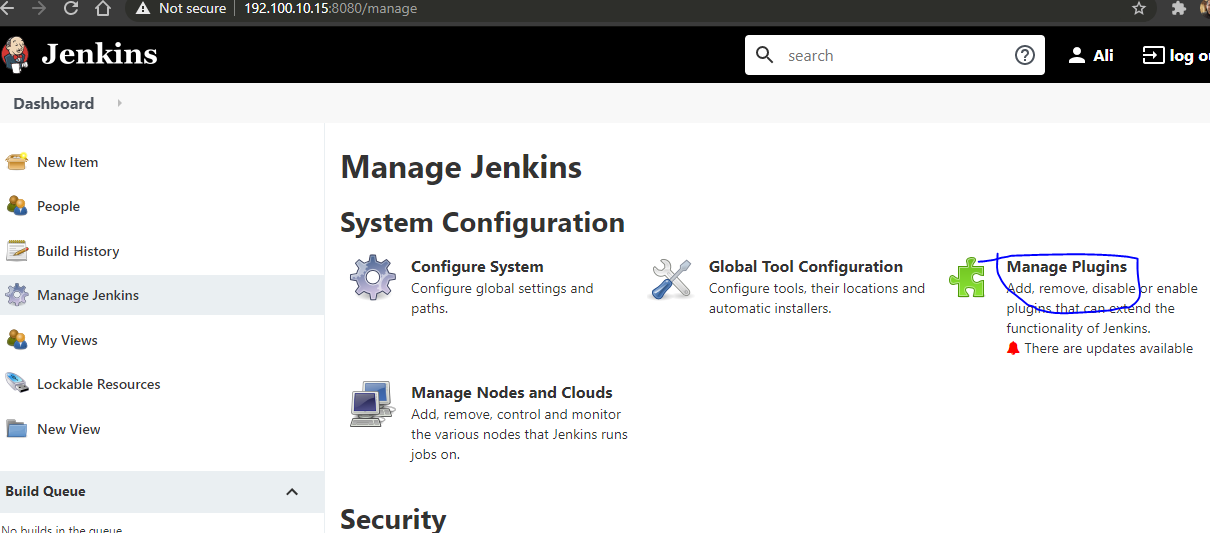
Jenkins, an autonomous Java-based application, is designed for immediate deployment across various operating systems like Windows, Mac OS X, and Unix-like systems. Functioning as a highly adaptable automation server, Jenkins serves as both a basic Continuous Integration (CI) server and a comprehensive continuous delivery center for diverse project requirements.
To establish and configure the Jenkins server within a Linux environment, the installation of Java is a prerequisite. The following steps outline the process:
- Java Installation Java is a mandatory component. Utilize the sudo user for Java installation.
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jre
sudo update-alternatives --config java- Jenkins Installation Initially, procure the Jenkins Binary suitable for debian Linux.
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
sudo apt-get updateProceed with the installation of Jenkins on the designated machine.
sudo apt-get install jenkins- Server Access
http://192.100.10.15:8080/
/var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
The installation and configuration of Jenkins on a Linux server necessitate the presence of Java. Following a structured sequence of commands, Java is first installed, then Jenkins is downloaded and set up. Post-installation, accessing the server involves retrieving the initial administrative password for further configuration.